Help: Risk Estimates
Risk estimates and settings (area 3 & 4)
This view displays an overview of several risk measures implemented in ARX
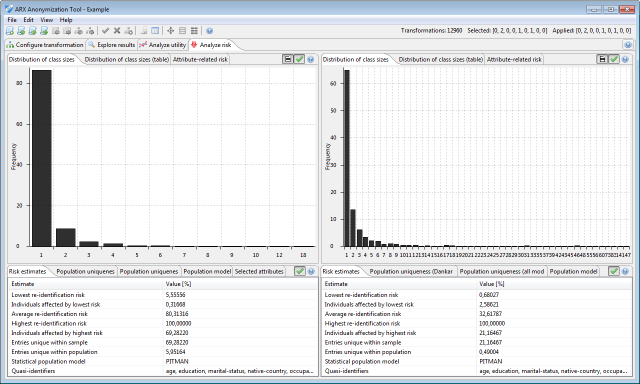
First, there are measures that are based on the sample itself, i.e., the size of the equivalence classes. These include:
- Lowest re-identification risk
- Individuals affected by lowest risk
- Highest re-identification risk
- Individuals affected by highest risk
- Average re-identification risk
- Fraction of unique tuples
Moreover, ARX supports estimating re-identification risks based on uniqueness determined via super-population models. These statistical methods estimate characteristics of the overall population with probability distributions that are parameterized with sample characteristics. We provide default settings for populations, such as the USA, UK, France or Germany, and support the methods by Pitman, Zayatz and the SNB model. The properties of the underlying population can be specified in this view.
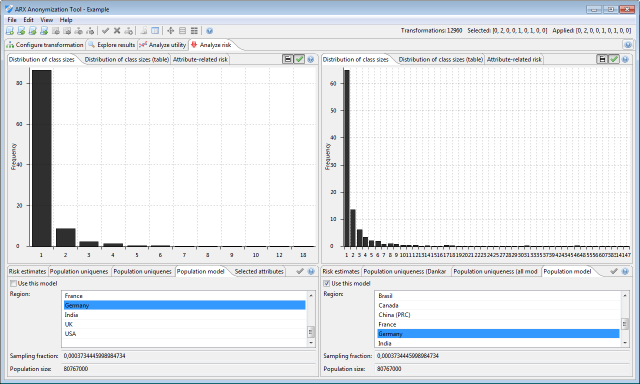
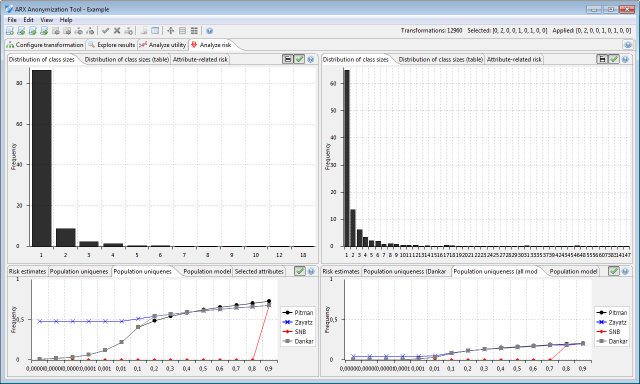
Different super-population models may return different estimates of population uniqueness. ARX also implements a decision rule proposed and validated for clinical datasets by Dankar et al. More information can be found here http://www.biomedcentral.com/1472-6947/12/66. In this view, the results of the methods by Pitman, Zayatz, the SNB model and the approach by Dankar may be compared for different sampling fractions.
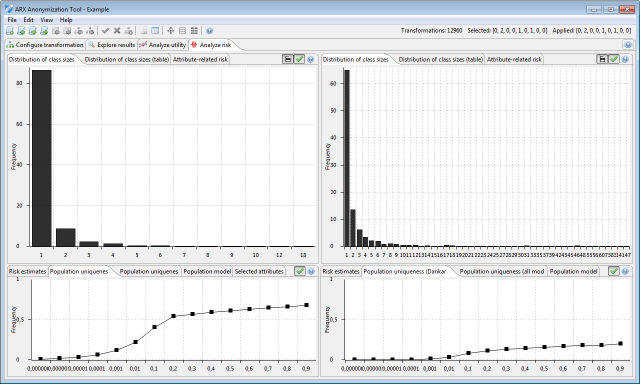
This view displays the resulting estimates by the method of Dankar et al., again, for different sampling fractions
For computing estimates from super-population models ARX must solve non-linear bivariate equation systems. The solver used by ARX can be configured in the settings dialog. Here, you may specify options such as the total number of iterations, iterations per try and the required accuracy etc. This may influence the precision of results and execution times.
