Overview
Configuration
Exploration
Utility analysis
Risk analysis
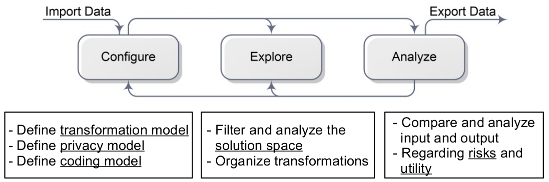
Overview of ARX's perspectives
ARX is divided into four perspectives, which model different aspects of the anonymization process. As is shown below, these perspectives support 1) configuring privacy models, utility measures and transformation methods, 2) exploring the solution space, 3) analyzing data utility and 4) analyzing privacy risks.
In the configuration perspective, input data can be loaded, transformation rules can be specified and all further parameters, such as privacy models and utility measures, can be selected and parameterized. If required, this step can be prepared by performing a risk analysis.
After the anonymization process, an overview of potential solutions can be inspected in the exploration perspective. Here, it is possible to search for privacy-preserving data transformations, which result in output data that is suited for the intended usage scenario. Please note that ARX will also automatically propose a solution.
To assess the usefulness of output data, the utility analysis perspective provides methods for comparing transformed data to input data using information loss models, descriptive statistics and application-specific analyses, e.g. focusing on machine learning tasks.
In the fourth perspective, privacy risks can be analyzed for input dataset as well as transformed output data. Based on the results of these analyses, the suitability of a solution candidate may either be confirmed or the parameters of the anonymization process can be modified, resulting in a semi-automated workflow.
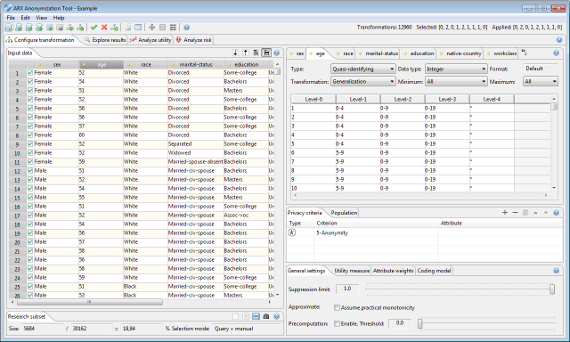
Configuration perspective
In the configuration perspective, data can be imported, transformation rules can be created, and privacy as well as quality models can be selected and parameterized. Input data is always displayed on the left hand side.
The data import wizard supports a variety of data sources and allows to specify meta data, such as data types and formats. ARX is able to import data from CSV files, MS Excel spreadsheets and relational database systems, such as MS SQL, DB2, MySQL or PostgreSQL.
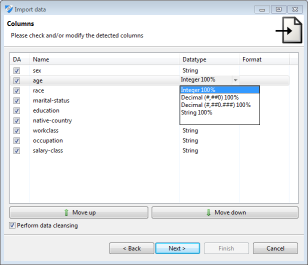
The data import wizard also supports the renaming, removing and reordering of columns. During data import, data types are automatically detected and data cleansing may be performed. This means that values that do not conform to the specified data type will be replaced with specific null values, which are handled correctly by all methods implemented in ARX.
All tabular data displayed by ARX can be exported into CSV files via context menus. ARX uses value generalization hierarchies to implement a wide variety of data transformation methods. These hierarchies can either be created within the software (via specific wizards) or imported from CSV files. Hierarchies created with ARX can also be exported to CSV files.
Exploration perspective
During the anonymization process, ARX characterizes a solution space of potential transformations of the input dataset. For each solution candidate it is determined whether risk thresholds are met and data quality is quantified according to the given model. This perspective allows users to browse the result of this process and to select interesting transformations for further analysis.
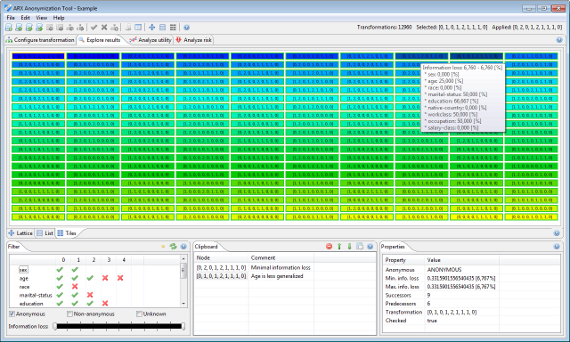
Please note that since version 3.7.0 ARX supports a local transformation method which applies different transformation schemes to different parts of the input dataset. In this case, the exploration perspective displays the individual transformations applied to the dataset.
Utility analysis perspective
The utility analysis perspective can be used to assess the suitability of a specific transformation for an anticipated usage scenario. For this purpose, input and transformed data are displayed side by side. Moreover, descriptive statistics can be calculated and the suitability of output data as a training set for creating classification models can be analyzed. A variety of graphical and numerical representations are displayed to aid interpretation.
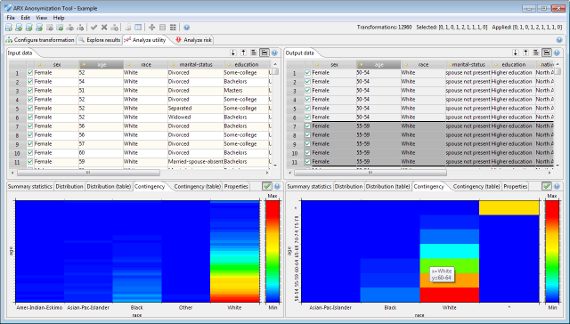
The utility analysis perspective also provides a view which can be used to apply local transformation to the output dataset. Please note that this functionality is typically not needed in ARX 3.7.0 or later and it may be removed in the future.
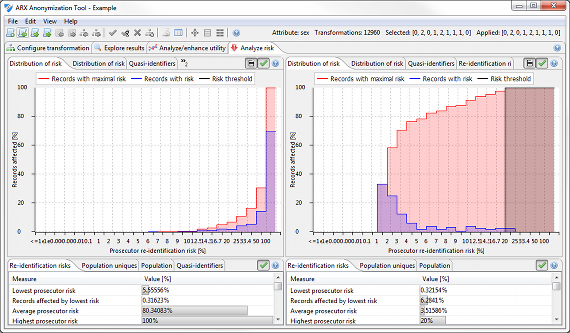
Risk analysis perspective
In this perspective, various metrics reflecting privacy risks are presented. Metrics implemented by ARX include re-identification risks for the prosecutor, journalist and marketer attacks as well as estimates of population uniqueness, which can be calculated using different statistical models. Moreover, the perspective also provides access to a method for detecting attributes which must be modified according to the Safe Harbor method of the US Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA identifiers) and a method for detecting further quasi-identifiers.